Nonlinear effects of wind on Atlantic ocean circulation
4.9 (613) · € 25.00 · En Stock
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is a system of ocean currents that transports warm, salty water from the tropics to the northern Atlantic. As the water cools, it becomes denser and sinks, in a process known as overturning. The cold deep water then flows back toward the equator. This process of transportation plays a critical role in Earth
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is a system of ocean currents that transports warm, salty water from the tropics to the northern Atlantic. As the water cools, it becomes denser and sinks, in a process known as overturning. The cold deep water then flows back toward the equator. This process of transportation plays a critical role in Earth's climate.
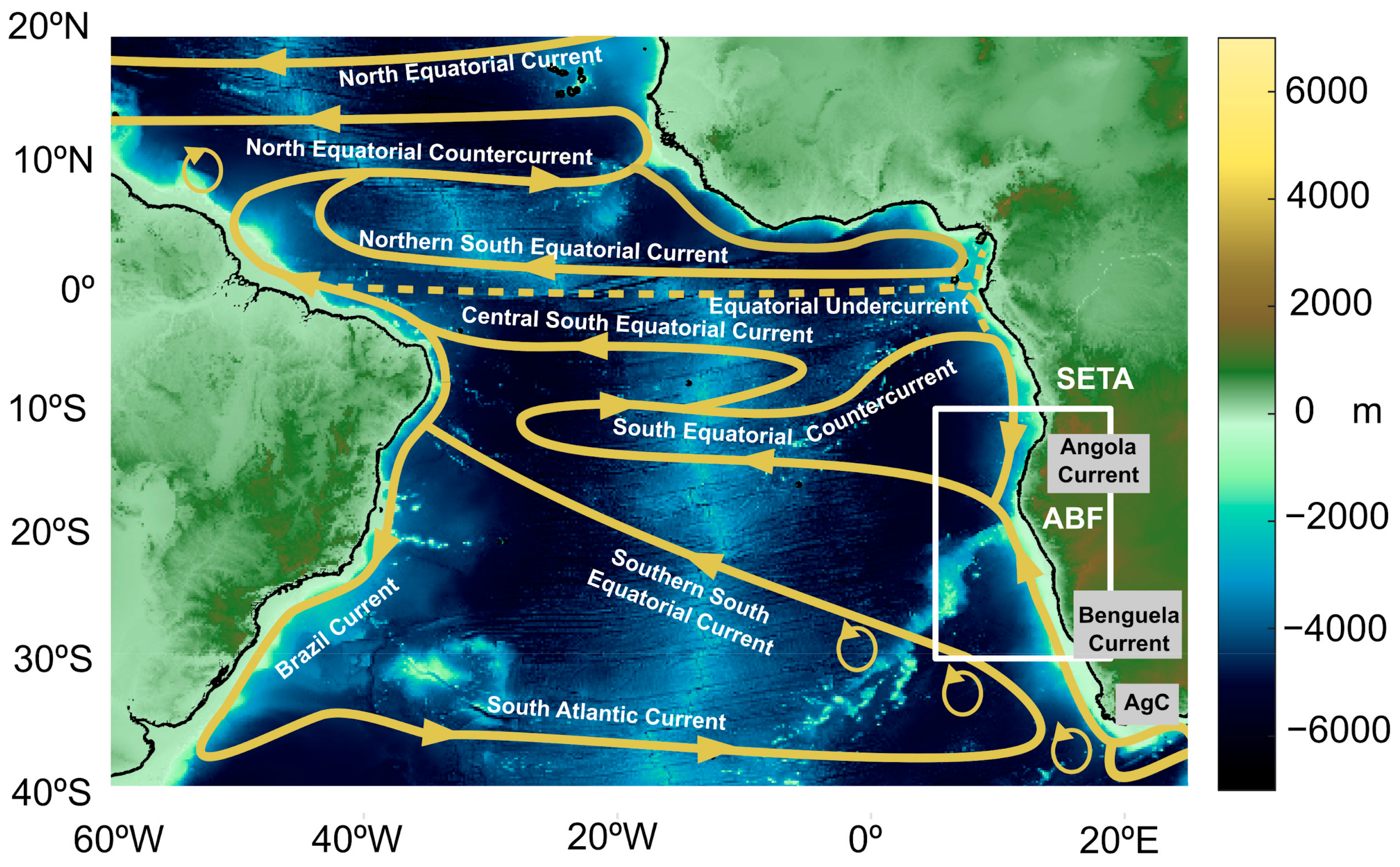
Atmosphere, Free Full-Text

Global map of sea level rise vs. non-linear effects For all sites, the
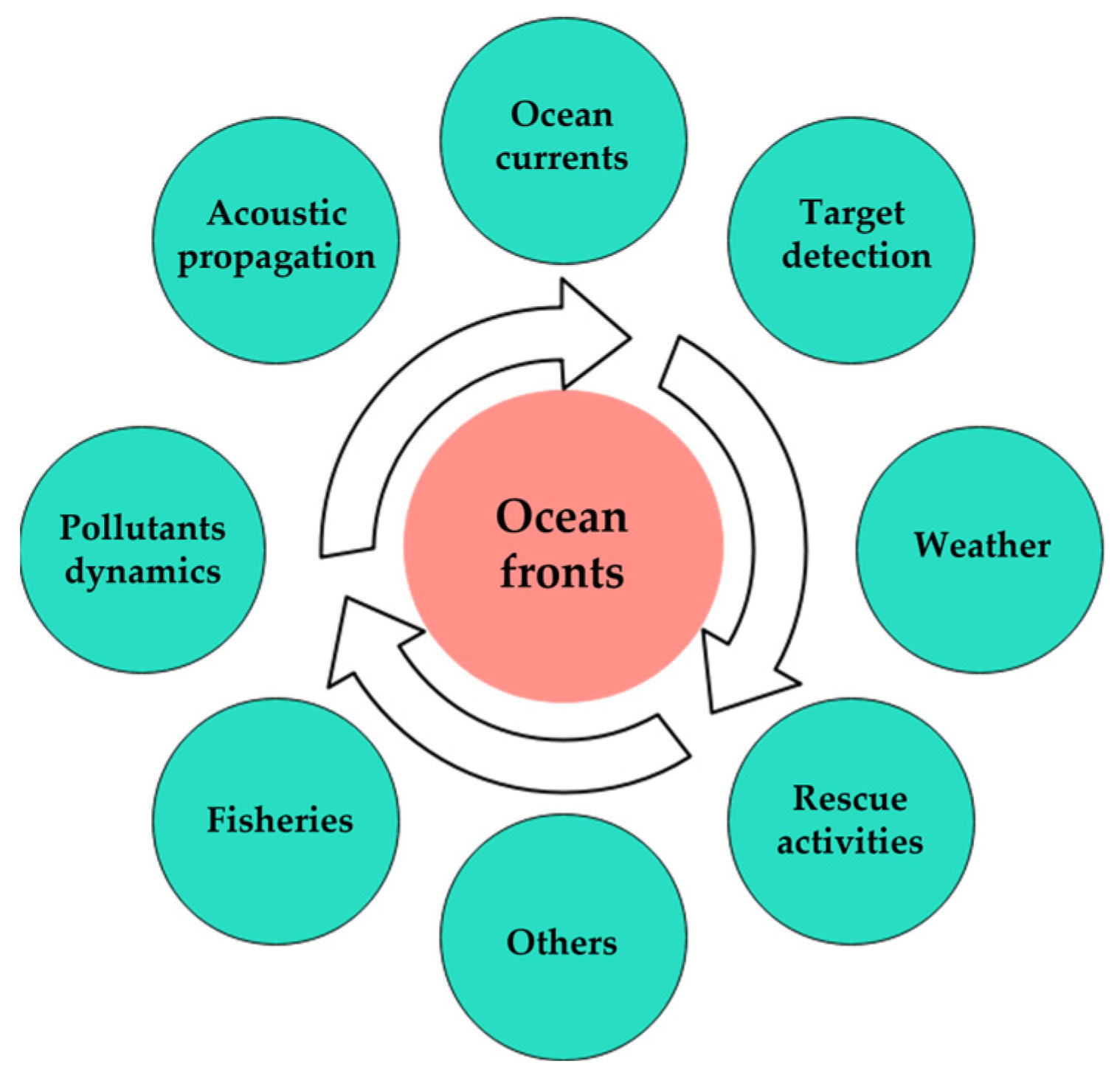
JMSE, Free Full-Text

Understanding Arctic Ocean Circulation: A Review of Ocean Dynamics in a Changing Climate - Timmermans - 2020 - Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans - Wiley Online Library
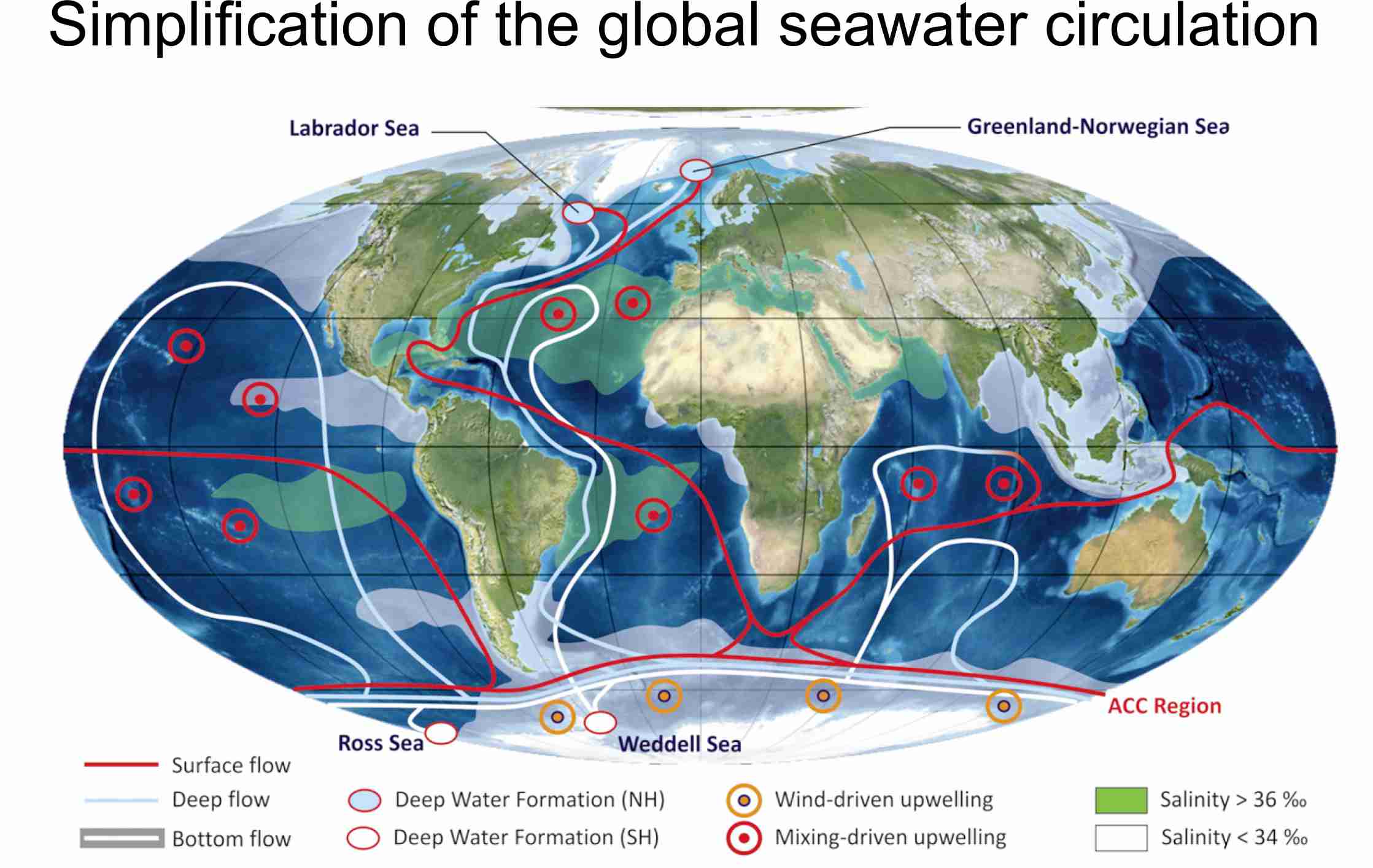
Stratigraphy, Sedimentology and Palaeontology Sediment in the deep ocean. Part 2: thermohaline currents that shape the seafloor

Full article: Nonlinear wind-drift ocean currents in arctic regions
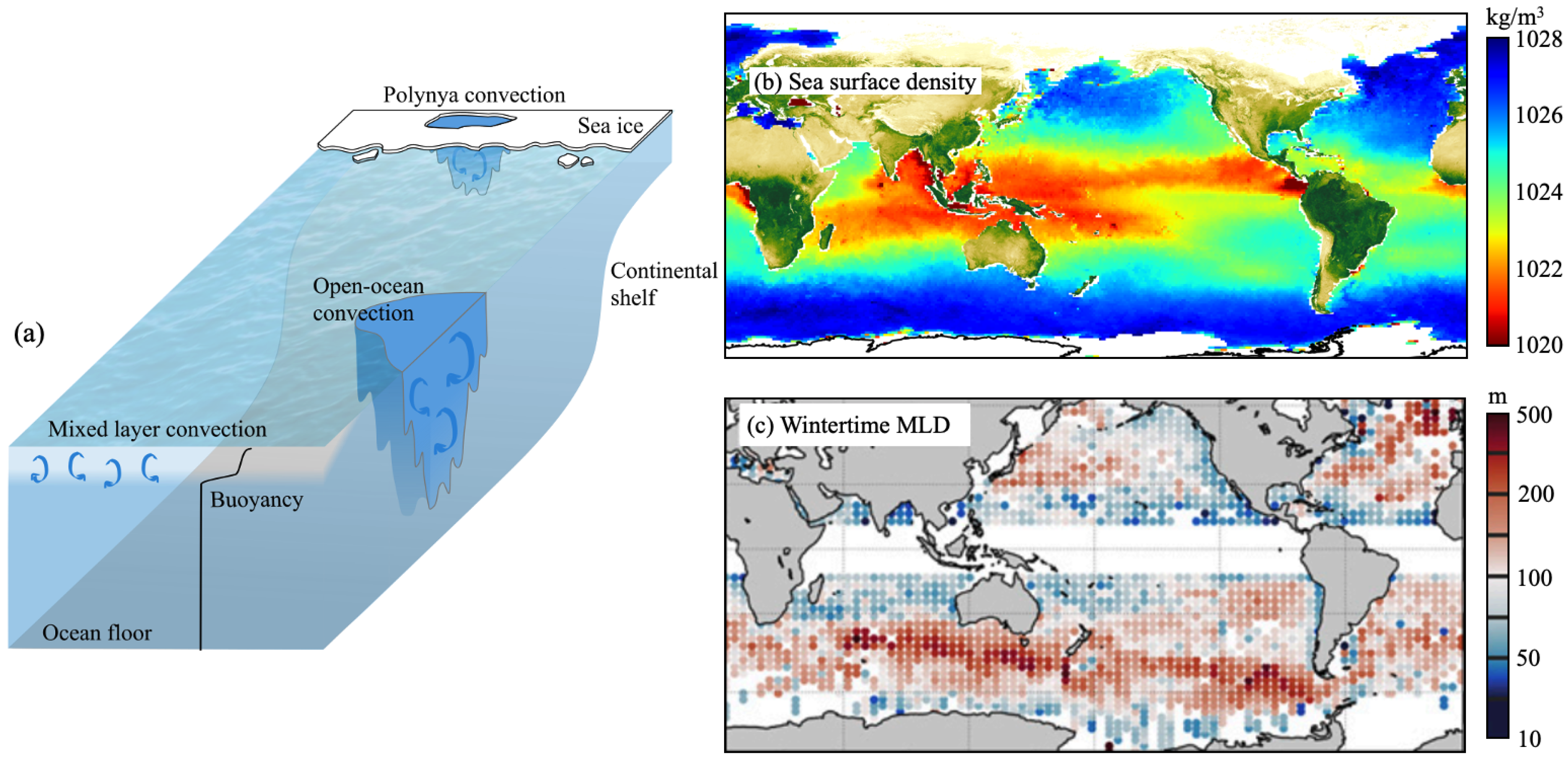
Fluids, Free Full-Text
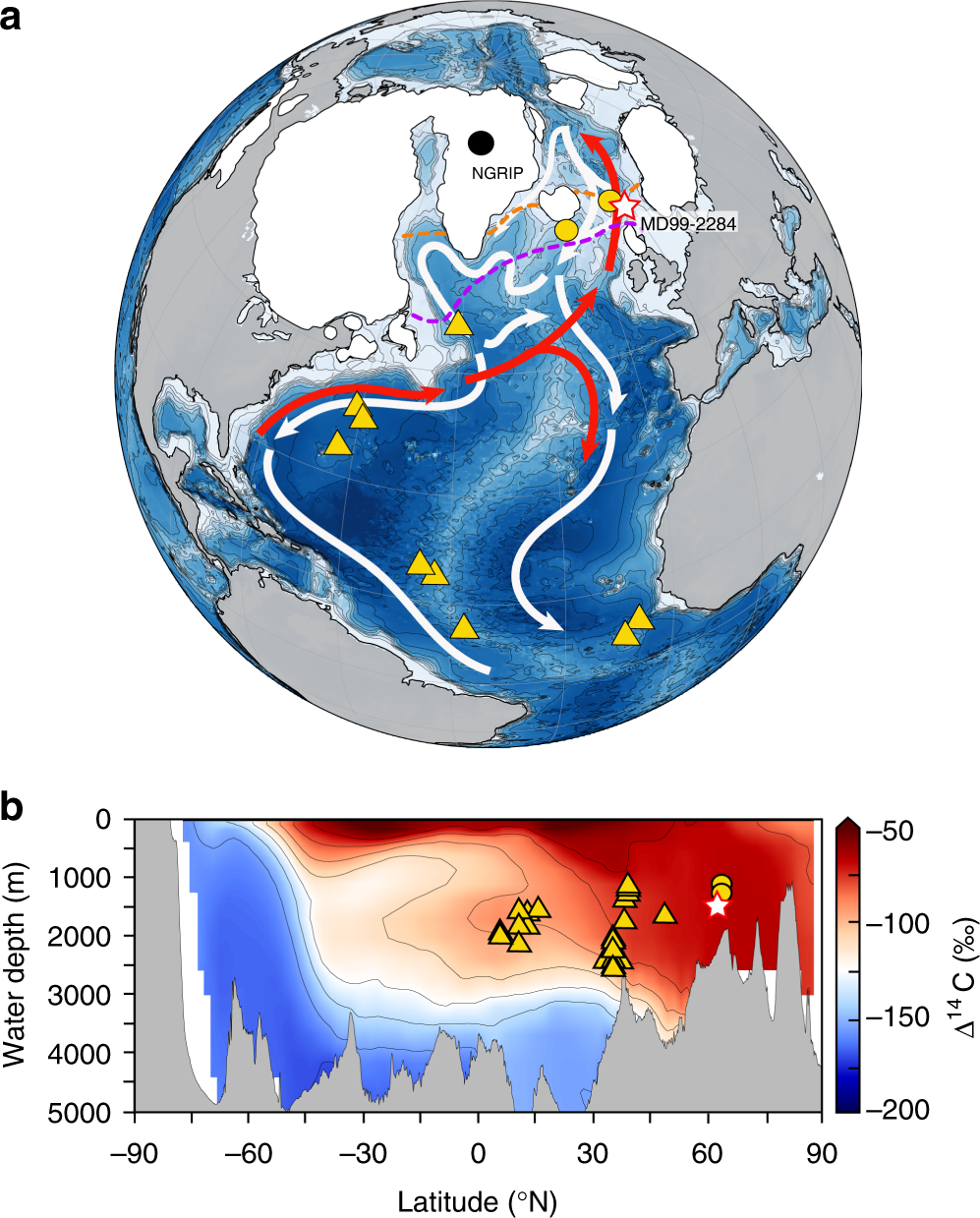
Deep-water circulation changes lead North Atlantic climate during deglaciation

Wind-Driven Circulation - an overview

OS - Water masses in the Atlantic Ocean: characteristics and distributions

The Relationship Between U.S. East Coast Sea Level and the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: A Review - Little - 2019 - Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans - Wiley Online Library

Full article: Frictional effects in wind-driven ocean currents
WCD - Nonlinearity in the tropospheric pathway of ENSO to the North Atlantic












